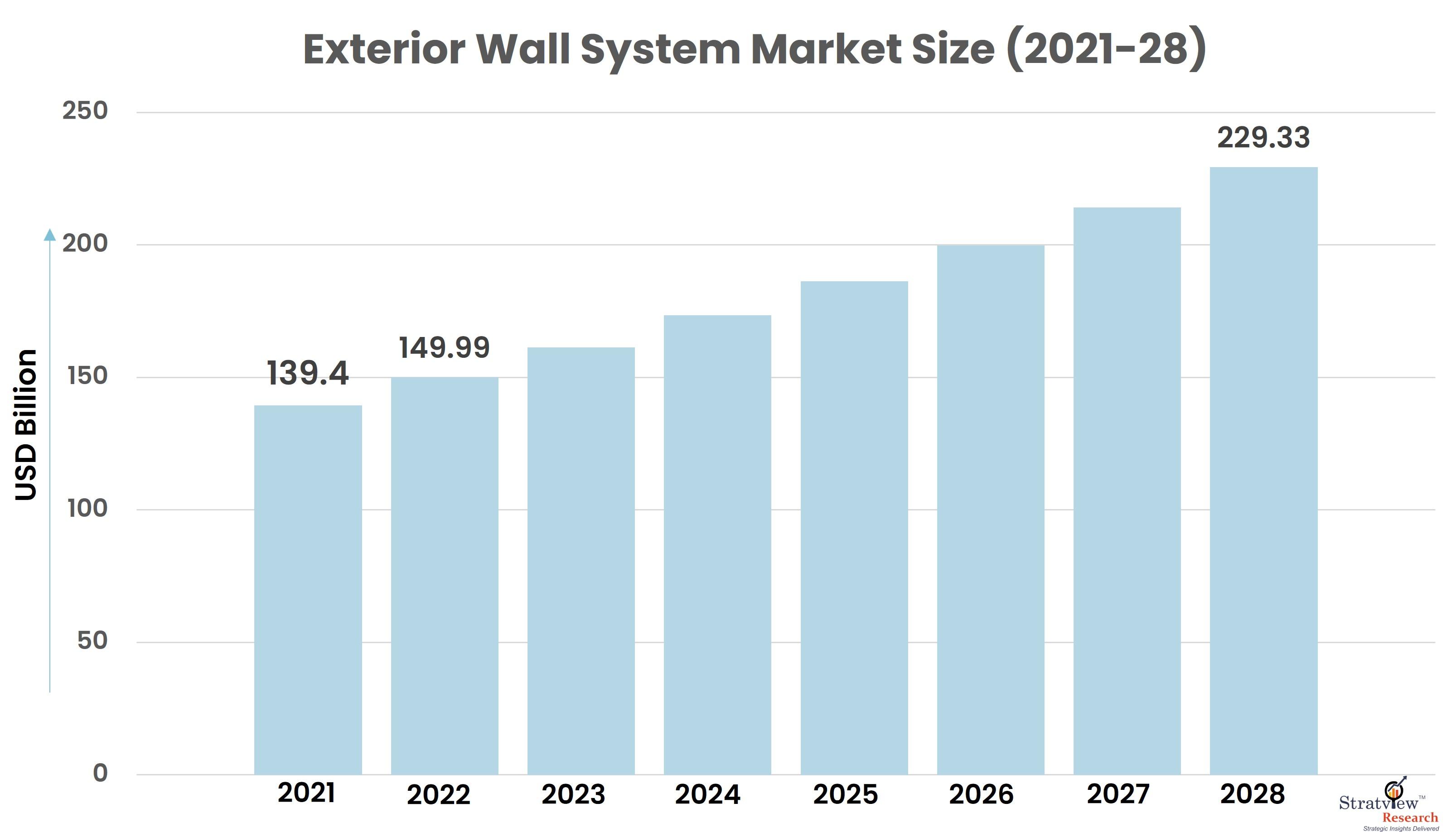
According to Stratview Research, the exterior wall system market was estimated at USD 139.4 billion in 2021 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 7.33% during 2022-2028 to reach USD 229.33 billion in 2028.
In the dynamic realm of architecture and construction, exterior wall systems are undergoing a profound evolution that transcends mere aesthetics. While the visual appeal of buildings remains essential, the contemporary focus on functionality, performance, and sustainability is propelling exterior wall systems into a new era. This shift signifies a departure from traditional design paradigms, heralding the rise of systems that not only enhance the visual identity of structures but also contribute to energy efficiency, resilience, and overall building functionality.
- Holistic Building Envelopes: Form Meets Function
The functional evolution of exterior wall systems revolves around the concept of holistic building envelopes. Beyond serving as a boundary between indoor and outdoor spaces, modern exterior walls are designed to function as dynamic, responsive elements that contribute to the overall performance of the building. This integration of form and function signifies a departure from conventional design practices towards a more holistic approach.
- Energy Efficiency as a Priority
One of the key drivers in the functional evolution of exterior wall systems is the imperative for energy efficiency. The emphasis on reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact has led to the development of high-performance insulation materials, advanced thermal barriers, and innovative designs that optimize the energy efficiency of buildings. Exterior walls are no longer passive elements but active contributors to sustainable building practices.
- Climate-Responsive Design
As climate change becomes a defining factor in architectural considerations, exterior wall systems are evolving to respond to climatic challenges. Climate-responsive design involves creating walls that adapt to seasonal variations, providing optimal insulation in colder months and promoting natural ventilation during warmer periods. This adaptability contributes to the overall comfort of occupants while reducing the building's environmental footprint.
- Resilience in the Face of Adversity
The functional evolution of exterior wall systems places a significant emphasis on resilience. Buildings are now expected to withstand a range of environmental challenges, from extreme weather events to natural disasters. Exterior walls are being engineered with materials and designs that enhance their resilience, ensuring the long-term durability and structural integrity of the building envelope.
- Integrated Technological Solutions
Technology is playing a pivotal role in the functional evolution of exterior wall systems. Integrated technological solutions, including smart sensors, climate monitoring systems, and dynamic shading devices, are becoming standard features. These innovations not only contribute to energy efficiency but also enhance occupant comfort by creating responsive environments that adapt to changing conditions.
- Sustainable Material Choices
Sustainability is a core tenet of the functional evolution of exterior wall systems. The choice of materials has shifted towards sustainable options, including recycled content, responsibly sourced timber, and innovative composites. This eco-conscious approach not only aligns with global efforts towards green building practices but also addresses the demand for environmentally friendly construction materials.
- Dynamic Facades for Natural Light Optimization
Natural light is a prized asset in architectural design, and exterior wall systems are evolving to optimize its benefits. Dynamic facades, incorporating features such as adjustable louvers, electrochromic glass, and light-diffusing materials, allow for the controlled entry of natural light. This not only enhances the visual appeal of interiors but also reduces the reliance on artificial lighting, contributing to energy savings.
- Acoustic Performance and Noise Reduction
The functional evolution of exterior wall systems extends to acoustic performance. As urban environments become increasingly noisy, especially in densely populated areas, the integration of sound-absorbing materials and specialized designs is becoming more prevalent. Exterior walls are now serving as protective barriers, mitigating noise pollution and creating quieter, more comfortable living and working spaces.
- Modular and Prefabricated Construction
The shift towards functional evolution includes changes in construction methods. Modular and prefabricated construction techniques are gaining prominence, allowing for the efficient assembly of exterior wall systems off-site. This approach not only streamlines the construction process but also ensures a higher level of precision, quality control, and cost-effectiveness.
- Enhanced Durability and Low Maintenance
Functionality in exterior wall systems also involves considerations of durability and low maintenance. The use of robust materials that resist weathering, corrosion, and degradation is a notable trend. By reducing the need for frequent repairs and maintenance, modern exterior walls contribute to the longevity and cost-effectiveness of buildings.
Conclusion: The Dawn of a Functional Aesthetic
As exterior wall systems undergo a functional evolution, the architecture of today is witnessing the dawn of a new era—a fusion of aesthetics and functionality that goes beyond the superficial. The emphasis on energy efficiency, resilience, sustainability, and technological integration is reshaping the very fabric of building design. Exterior walls are no longer passive elements; they are dynamic contributors to the performance, comfort, and longevity of structures. The functional evolution of exterior wall systems is not just a trend; it's a fundamental shift towards a future where buildings are not only visually striking but also intelligent, sustainable, and resilient. In this paradigm, exterior walls become the canvas upon which the functional aesthetic of the modern built environment is painted.