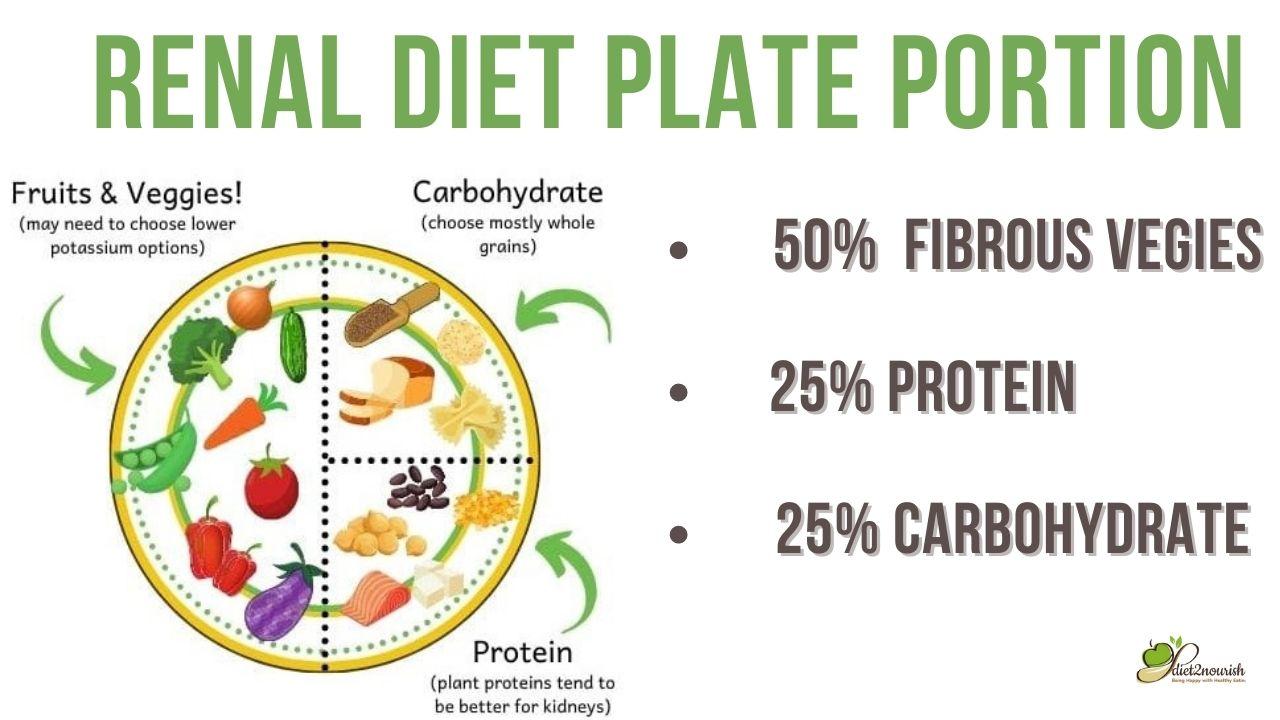
A well-structured diet is a crucial component of managing kidney disease, and for Indian kidney patients, dietary choices play a significant role in preserving kidney function, managing symptoms, and improving overall well-being.
Understanding Kidney Disease: Kidneys are vital organs that play a central role in filtering waste products, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood, while also maintaining electrolyte balance and regulating blood pressure. Kidney disease, also known as renal disease or nephropathy, occurs when the kidneys' function is impaired. It can result from various factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, infections, and other medical conditions.
Importance of Kidney Health: Healthy kidneys are essential for overall well-being. When kidney function declines, waste products and excess fluids accumulate in the body, leading to symptoms like fatigue, swelling, high blood pressure, and anemia. Effective management of kidney disease, including dietary choices, can slow its progression and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Dietary Guidelines for Indian Diet Chart for Kidney Patients An Indian diet chart for kidney patients should focus on supporting kidney function while managing symptoms and maintaining overall health. Here are key dietary guidelines:
-
Limit Protein Intake: Reduce the consumption of high-protein foods, especially animal-based proteins like meat, poultry, and fish. Opt for plant-based proteins like legumes, tofu, and dairy in moderation.
-
Control Sodium (Salt) Intake: Lower sodium intake to help manage fluid balance and blood pressure. Avoid adding extra salt to meals, and limit the consumption of processed and restaurant foods, which often contain high levels of sodium.
-
Monitor Phosphorus and Potassium: High levels of phosphorus and potassium can be problematic for kidney patients. Be mindful of foods rich in these minerals, such as dairy products, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and certain fruits and vegetables. It may be necessary to limit or avoid some of these foods, depending on individual needs.
-
Stay Hydrated: Maintain proper hydration, but avoid excessive fluid intake, as impaired kidneys may struggle to eliminate excess fluids. Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations regarding fluid intake, and adjust it based on your individual requirements.
-
Choose High-Quality Protein Sources: If you include protein in your diet, prioritize high-quality sources like tofu, legumes, dairy, and limited amounts of lean meats or fish.
-
Reduce Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates: Minimize the consumption of sugary snacks, desserts, and beverages, as well as refined carbohydrates like white bread and sugary cereals. Choose whole grains and complex carbohydrates instead.
-
Monitor Phosphorus: Be aware of phosphorus-rich foods, including dairy products, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and processed foods. In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend phosphorus binders to control phosphorus levels.
Foods to Include in an Indian Diet Chart for Kidney Patients
-
Rice: Rice is a staple in Indian cuisine and is generally a suitable source of carbohydrates for kidney patients.
-
Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and kidney beans are good sources of plant-based protein for kidney patients.
-
Tofu: Tofu is a versatile source of plant-based protein that can be used in various Indian dishes.
-
Low-Potassium Vegetables: Include low-potassium vegetables like bottle gourd (lauki), ridge gourd (torai), and ivy gourd (tindora) in your diet.
-
Cauliflower: Cauliflower is a versatile vegetable that can be used in various Indian dishes and is low in potassium.
-
Paneer: Paneer (Indian cottage cheese) is a moderate-protein, low-phosphorus dairy option for kidney patients.
-
Spices and Herbs: Indian spices like turmeric, cumin, coriander, and fenugreek can add flavor to dishes without adding excess sodium.
-
Fruits: Apples, pears, and cranberries are among the fruits that are generally safe for kidney patients when consumed in moderation.
-
Ghee: In limited quantities, clarified butter (ghee) can be used in cooking to add flavor without the excess saturated fats found in regular butter.
Foods to Limit or Avoid:
-
High-Protein Meats: Reduce the consumption of high-protein meats like mutton and organ meats.
-
High-Potassium Foods: Limit or avoid high-potassium foods like bananas, oranges, potatoes, tomatoes, and spinach.
-
High-Phosphorus Foods: Be cautious with foods rich in phosphorus, including dairy products, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and processed foods.
-
Processed Foods: Minimize processed and packaged foods, as they often contain high levels of sodium, phosphorus additives, and preservatives.
-
Salt and Sodium: Avoid adding extra salt to your meals, and choose low-sodium or no-added-salt products.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Kidney Disease: In addition to dietary considerations, lifestyle habits are essential for effectively managing kidney disease:
-
Medication Compliance: If prescribed medications, take them as directed by your healthcare provider.
-
Regular Monitoring: Follow up with your healthcare provider regularly to assess kidney function and adjust treatment or dietary recommendations as needed.
-
Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity as recommended by your healthcare provider to support overall health.
-
Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep, as it plays a vital role in overall well-being.
-
Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to minimize the impact of stress on kidney function.
-
Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, consider quitting, as smoking can worsen kidney disease and increase the risk of complications.
-
Limit Alcohol: Consume alcohol in moderation or as advised by your healthcare provider, as excessive alcohol can strain the kidneys.
It's crucial to remember that managing kidney disease through diet and lifestyle requires individualized care and recommendations. Therefore, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian who specializes in kidney health for personalized guidance and to ensure that dietary changes align with your unique health goals and needs.